Manual Interoperability: Why It's Time to Switch to Automated Testing
While traditional methods of manual interoperability testing have commendable advantages, they have been facing increasing criticism in recent times. They offer swift implementation and prove ideal for the execution of preliminary 'smoke' tests, designed specifically to validate the resolution of earlier identified problems. These methods also provide valuable insights into the user experience, granting engineers and Quality Assurance (QA) professionals the ability to step into the shoes of their consumers and view the product from their perspective.
However, despite the aforementioned benefits, the manual approach to interoperability testing is plagued with an array of challenges.
Manual testing has an inherent limitation - there's a finite extent to which it can be utilised before it becomes impractical to evaluate every conceivable use case and variation. With the world producing of millions of connected devices each year and the complexity of use cases escalating at an unprecedented rate, a strategy that relies solely on manual testing is likely to overlook various issues and vulnerabilities.
Businesses that continue to stick with a purely manual approach run the risk of exposing themselves to a variety of potential complications. Why is this the case? The answer lies in the inherent shortcomings of manual testing. The scalability of manual testing does not meet the rigorous demands of modern product release timelines. Additionally, it is restrained by human limitations in accurately identifying issues and locating the root cause when bugs emerge.
Identical issues can often pass unnoticed during manual testing due to the sheer volume of tests required, and factors such as the difficulty of recognising bugs versus expected behaviours. It is here that the potential of automated testing comes to the fore, providing deeper insights that can significantly enhance the quality of devices and products, making them as bug-free as possible.
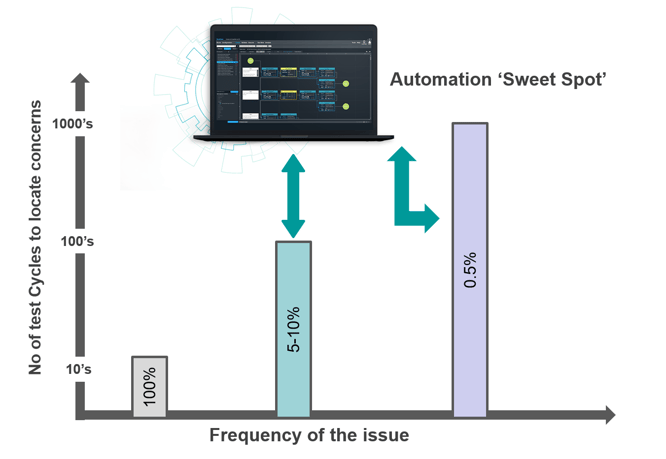
Here, we delve into three common issues that may surface but can prove challenging to trace and resolve - unless automation comes into the picture.
Issue 1: Invisible Data Retransmissions
The resilience of modern device connectivity has been revolutionised by the capability to retransmit data until successful delivery. It's an invaluable feature that ensures data integrity and reliability. However, manual testing might fail to pick up on these 'hidden' data retransmissions. This can lead engineers to mistakenly record successful tests in marginal conditions, remaining oblivious to potential real-world failures that could have disastrous consequences.
Automated interoperability testing, by contrast, offers a higher degree of scrutiny. It can effectively detect marginal conditions and flag repetitive retransmissions, thereby providing product developers with early warnings of potential issues that could affect the product's performance on a larger scale.
Issue 2: Coexistence Complications
In most contemporary products, the coexistence of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi is managed automatically. However, this seamless coexistence can be disrupted, especially when an antenna is required to perform double duty for both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
Additional problems can emerge when transmitters and receivers are situated in close proximity, causing signal overlap or interference. Undertaking manual testing of all these potential permutations and combinations is beyond the capacity of even the most dedicated human team. Hence, automation emerges as the swiftest, most reliable, and effective means of assuring your product's ability to manage coexistence issues.
Issue 3: The Manifestation of Intermittent Bugs
Manual testing has a tendency to uncover only the issues or failures that occur most frequently. The less frequent, yet significant problems that can cause considerable frustration to users, often slip through the cracks. This is where automated interoperability testing can provide the additional test case coverage required to generate insights into these less common but still problematic failures.
Automated testing also has the capability to unearth bugs hidden within complex test scenarios involving a multitude of variables, something that manual testing would struggle to achieve effectively, if at all, due to the need to minimise variables in manual testing.
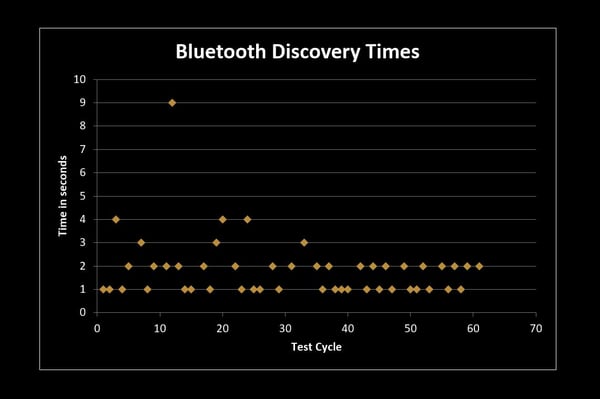
The diagram below illustrates the substantial benefits of increasing the frequency of each test. External factors, while relatively rare, can significantly impact user experiences. For instance, in this 60+ cycle test, most Bluetooth Discovery connections were established in two seconds. However, there were several discovery cycles that were twice as long and one discovery connection took an unusually long 9 seconds, which would almost certainly have been missed with limited manual tests.
Unlocking the Potential of Automated Interoperability Testing
The inherent benefits of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi automated interoperability testing are unquestionable. By extending test scenarios to realms far beyond the capabilities of manual testing, automated testing produces valuable insights and results that manual testing would struggle to achieve.
Successfully resolving coexistence complications, effectively managing concealed data retransmissions, and gaining an in-depth understanding of the manifestation of bugs are integral aspects of successfully launching a new product in today's hyper-competitive market. Automation emerges as the sole reliable method to ensure comprehensive coverage of all these aspects, paving the way for product success and consumer satisfaction.
Automated product test platforms, such as Nextgen ATAM Connect can assist in building an automated end-to-end test capability within days. By integrating automated interoperability testing into the development process, either on site or working with external partners like Nextgen, companies developing connected products can ensure interoperability with technologies anywhere in the world and deliver a seamless customer experience.
For more information about our testing services and how Nextgen can support your product development, please contact us today or call +44 3331 120 000.




